- class QDockWidget#
The
QDockWidgetclass provides a widget that can be docked inside aQMainWindowor floated as a top-level window on the desktop. More…Synopsis#
Properties#
allowedAreasᅟ- Areas where the dock widget may be placedfeaturesᅟ- Whether the dock widget is movable, closable, and floatablefloatingᅟ- Whether the dock widget is floatingwindowTitleᅟ- The dock widget title (caption)
Methods#
def
__init__()def
allowedAreas()def
features()def
isAreaAllowed()def
isFloating()def
setFeatures()def
setFloating()def
setWidget()def
titleBarWidget()def
widget()
Virtual methods#
Signals#
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description#
QDockWidgetprovides the concept of dock widgets, also know as tool palettes or utility windows. Dock windows are secondary windows placed in the dock widget area around thecentral widgetin aQMainWindow.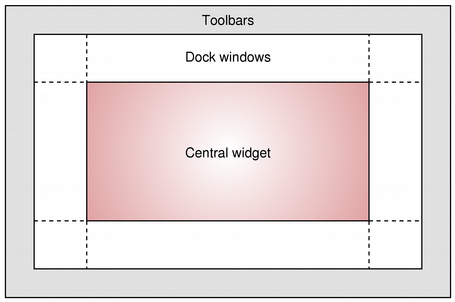
Dock windows can be moved inside their current area, moved into new areas and floated (e.g., undocked) by the end-user. The
QDockWidgetAPI allows the programmer to restrict the dock widgets ability to move, float and close, as well as the areas in which they can be placed.Appearance#
A
QDockWidgetconsists of a title bar and the content area. The title bar displays the dock widgetswindow title, a float button and a close button. Depending on the state of theQDockWidget, the float and close buttons may be either disabled or not shown at all.The visual appearance of the title bar and buttons is dependent on the
stylein use.A
QDockWidgetacts as a wrapper for its child widget, set withsetWidget(). Custom size hints, minimum and maximum sizes and size policies should be implemented in the child widget.QDockWidgetwill respect them, adjusting its own constraints to include the frame and title. Size constraints should not be set on theQDockWidgetitself, because they change depending on whether it is docked; a dockedQDockWidgethas no frame and a smaller title bar.Note
On macOS, if the
QDockWidgethas a native window handle (for example, ifwinId()is called on it or the child widget), then due to a limitation it will not be possible to drag the dock widget when undocking. Starting the drag will undock the dock widget, but a second drag will be needed to move the dock widget itself.See also
- class DockWidgetFeature#
Constant
Description
QDockWidget.DockWidgetClosable
(inherits
enum.Flag) The dock widget can be closed.QDockWidget.DockWidgetMovable
The dock widget can be moved between docks by the user.
QDockWidget.DockWidgetFloatable
The dock widget can be detached from the main window, and floated as an independent window.
QDockWidget.DockWidgetVerticalTitleBar
The dock widget displays a vertical title bar on its left side. This can be used to increase the amount of vertical space in a
QMainWindow.QDockWidget.NoDockWidgetFeatures
The dock widget cannot be closed, moved, or floated.
Note
Properties can be used directly when
from __feature__ import true_propertyis used or via accessor functions otherwise.- property allowedAreasᅟ: Combination of Qt.DockWidgetArea#
This property holds areas where the dock widget may be placed.
The default is Qt::AllDockWidgetAreas.
See also
DockWidgetArea- Access functions:
- property featuresᅟ: Combination of QDockWidget.DockWidgetFeature#
This property holds whether the dock widget is movable, closable, and floatable.
By default, this property is set to a combination of
DockWidgetClosable,DockWidgetMovableandDockWidgetFloatable.See also
- Access functions:
- property floatingᅟ: bool#
This property holds whether the dock widget is floating.
A floating dock widget is presented to the user as a single, independent window “on top” of its parent
QMainWindow, instead of being docked either in theQMainWindow, or in a group of tabbed dock widgets.Floating dock widgets can be individually positioned and resized, both programmatically or by mouse interaction.
By default, this property is
true.When this property changes, the
topLevelChanged()signal is emitted.See also
- Access functions:
- property windowTitleᅟ: str#
This property holds the dock widget title (caption).
By default, this property contains an empty string.
Access functions:
- __init__(title[, parent=None[, flags=Qt.WindowFlags()]])#
- Parameters:
title – str
parent –
QWidgetflags – Combination of
WindowType
Constructs a
QDockWidgetwith parentparentand window flagsflags. The dock widget will be placed in the left dock widget area.The window title is set to
title. This title is used when theQDockWidgetis docked and undocked. It is also used in the context menu provided byQMainWindow.See also
- __init__([parent=None[, flags=Qt.WindowFlags()]])
- Parameters:
parent –
QWidgetflags – Combination of
WindowType
Constructs a
QDockWidgetwith parentparentand window flagsflags. The dock widget will be placed in the left dock widget area.- allowedAreas()#
- Return type:
Combination of
DockWidgetArea
See also
Getter of property
allowedAreasᅟ.- allowedAreasChanged(allowedAreas)#
- Parameters:
allowedAreas – Combination of
DockWidgetArea
This signal is emitted when the
allowedAreasproperty changes. TheallowedAreasparameter gives the new value of the property.Notification signal of property
allowedAreasᅟ.- dockLocationChanged(area)#
- Parameters:
area –
DockWidgetArea
This signal is emitted when the dock widget is moved to another dock
area, or is moved to a different location in its current dock area. This happens when the dock widget is moved programmatically or is dragged to a new location by the user.- features()#
- Return type:
Combination of
DockWidgetFeature
See also
Getter of property
featuresᅟ.- featuresChanged(features)#
- Parameters:
features – Combination of
DockWidgetFeature
This signal is emitted when the
featuresproperty changes. Thefeaturesparameter gives the new value of the property.Notification signal of property
featuresᅟ.- initStyleOption(option)#
- Parameters:
option –
QStyleOptionDockWidget
Initialize
optionwith the values from thisQDockWidget. This method is useful for subclasses when they need aQStyleOptionDockWidget, but don’t want to fill in all the information themselves.See also
- isAreaAllowed(area)#
- Parameters:
area –
DockWidgetArea- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif this dock widget can be placed in the givenarea; otherwise returnsfalse.- isFloating()#
- Return type:
bool
Getter of property
floatingᅟ.- setAllowedAreas(areas)#
- Parameters:
areas – Combination of
DockWidgetArea
See also
Setter of property
allowedAreasᅟ.- setFeatures(features)#
- Parameters:
features – Combination of
DockWidgetFeature
See also
Setter of property
featuresᅟ.- setFloating(floating)#
- Parameters:
floating – bool
See also
Setter of property
floatingᅟ.Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
Sets an arbitrary
widgetas the dock widget’s title bar. IfwidgetisNone, any custom title bar widget previously set on the dock widget is removed, but not deleted, and the default title bar will be used instead.If a title bar widget is set,
QDockWidgetwill not use native window decorations when it is floated.Here are some tips for implementing custom title bars:
Mouse events that are not explicitly handled by the title bar widget must be ignored by calling QMouseEvent::ignore(). These events then propagate to the
QDockWidgetparent, which handles them in the usual manner, moving when the title bar is dragged, docking and undocking when it is double-clicked, etc.When
DockWidgetVerticalTitleBaris set onQDockWidget, the title bar widget is repositioned accordingly. InresizeEvent(), the title bar should check what orientation it should assume:dockWidget = QDockWidget(parentWidget()) if dockWidget.features() QDockWidget.DockWidgetVerticalTitleBar: # I need to be vertical else: # I need to be horizontal
The title bar widget must have a valid
sizeHint()andminimumSizeHint(). These functions should take into account the current orientation of the title bar.It is not possible to remove a title bar from a dock widget. However, a similar effect can be achieved by setting a default constructed
QWidgetas the title bar widget.
Using qobject_cast() as shown above, the title bar widget has full access to its parent
QDockWidget. Hence it can perform such operations as docking and hiding in response to user actions.Sets the widget for the dock widget to
widget.If the dock widget is visible when
widgetis added, you mustshow()it explicitly.Note that you must add the layout of the
widgetbefore you call this function; if not, thewidgetwill not be visible.See also
Returns the custom title bar widget set on the
QDockWidget, orNoneif no custom title bar has been set.See also
Returns a checkable action that can be added to menus and toolbars so that the user can show or close this dock widget.
The action’s text is set to the dock widget’s window title.
Note
The action can not be used to programmatically show or hide the dock widget. Use the
visibleproperty for that.See also
- topLevelChanged(topLevel)#
- Parameters:
topLevel – bool
This signal is emitted when the
floatingproperty changes. ThetopLevelparameter is true if the dock widget is now floating; otherwise it is false.See also
- visibilityChanged(visible)#
- Parameters:
visible – bool
This signal is emitted when the dock widget becomes
visible(or invisible). This happens when the widget is hidden or shown, as well as when it is docked in a tabbed dock area and its tab becomes selected or unselected.Note
The signal can differ from
isVisible(). This can be the case, if a dock widget is minimized or tabified and associated to a non-selected or inactive tab.Returns the widget for the dock widget. This function returns zero if the widget has not been set.
See also