- class QLine#
The
QLineclass provides a two-dimensional vector using integer precision. More…Synopsis#
Methods#
def
__init__()def
__reduce__()def
__repr__()def
center()def
dx()def
dy()def
isNull()def
__ne__()def
__mul__()def
__eq__()def
p1()def
p2()def
setLine()def
setP1()def
setP2()def
setPoints()def
toLineF()def
toTuple()def
translate()def
translated()def
x1()def
x2()def
y1()def
y2()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description#
A
QLinedescribes a finite length line (or a line segment) on a two-dimensional surface. The start and end points of the line are specified using integer point accuracy for coordinates. Use theQLineFconstructor to retrieve a floating point copy.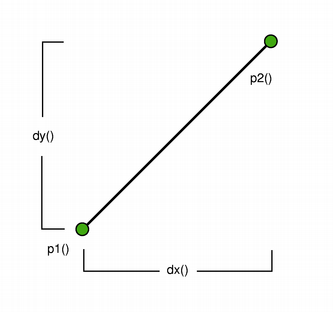
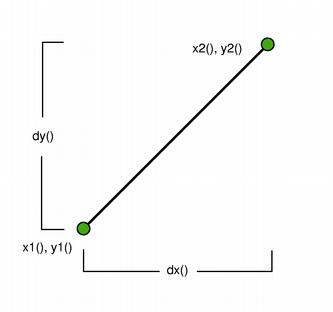
The positions of the line’s start and end points can be retrieved using the
p1(),x1(),y1(),p2(),x2(), andy2()functions. Thedx()anddy()functions return the horizontal and vertical components of the line. UseisNull()to determine whether theQLinerepresents a valid line or a null line.Finally, the line can be translated a given offset using the
translate()function.Constructs a line object that represents the line between
p1andp2.- __init__(x1, y1, x2, y2)
- Parameters:
x1 – int
y1 – int
x2 – int
y2 – int
Constructs a line object that represents the line between (
x1,y1) and (x2,y2).- __init__()
Constructs a null line.
- __reduce__()#
- Return type:
object
- __repr__()#
- Return type:
object
Returns the center point of this line. This is equivalent to (
p1()+p2()) / 2, except it will never overflow.- dx()#
- Return type:
int
Returns the horizontal component of the line’s vector.
See also
- dy()#
- Return type:
int
Returns the vertical component of the line’s vector.
See also
- isNull()#
- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueif the line does not have distinct start and end points; otherwise returnsfalse.Returns
trueif the givenlineis not the same as this line.A line is different from another line if any of their start or end points differ, or the internal order of the points is different.
- __mul__(m)#
- Parameters:
m –
QTransform- Return type:
Returns
trueif the givenlineis the same as this line.A line is identical to another line if the start and end points are identical, and the internal order of the points is the same.
Returns the line’s start point.
Returns the line’s end point.
- setLine(x1, y1, x2, y2)#
- Parameters:
x1 – int
y1 – int
x2 – int
y2 – int
Sets this line to the start in
x1,y1and end inx2,y2.Sets the starting point of this line to
p1.Sets the end point of this line to
p2.Sets the start point of this line to
p1and the end point of this line top2.Returns this line as a line with floating point accuracy.
See also
- toTuple()#
- Return type:
object
Translates this line by the given
offset.- translate(dx, dy)
- Parameters:
dx – int
dy – int
This is an overloaded function.
Translates this line the distance specified by
dxanddy.Returns this line translated by the given
offset.- translated(dx, dy)
- Parameters:
dx – int
dy – int
- Return type:
This is an overloaded function.
Returns this line translated the distance specified by
dxanddy.- x1()#
- Return type:
int
Returns the x-coordinate of the line’s start point.
See also
- x2()#
- Return type:
int
Returns the x-coordinate of the line’s end point.
See also
- y1()#
- Return type:
int
Returns the y-coordinate of the line’s start point.
See also
- y2()#
- Return type:
int
Returns the y-coordinate of the line’s end point.
See also