- class QLowEnergyService#
The
QLowEnergyServiceclass represents an individual service on a Bluetooth Low Energy Device. More…Synopsis#
Methods#
def
characteristic()def
contains()def
error()def
readDescriptor()def
serviceName()def
serviceUuid()def
state()def
type()
Signals#
def
descriptorRead()def
errorOccurred()def
stateChanged()
Note
This documentation may contain snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python. We always welcome contributions to the snippet translation. If you see an issue with the translation, you can also let us know by creating a ticket on https:/bugreports.qt.io/projects/PYSIDE
Detailed Description#
Warning
This section contains snippets that were automatically translated from C++ to Python and may contain errors.
QLowEnergyServiceprovides access to the details of Bluetooth Low Energy services. The class facilitates the discovery and publification of service details, permits reading and writing of the contained data and notifies about data changes.Service Structure#
A Bluetooth Low Energy peripheral device can contain multiple services. In turn each service may include further services. This class represents a single service of the peripheral device and is created via
createServiceObject(). Thetype()indicates whether this service is a primary (top-level) service or whether the service is part of another service. Each service may contain one or more characteristics and each characteristic may contain descriptors. The resulting structure may look like the following diagram: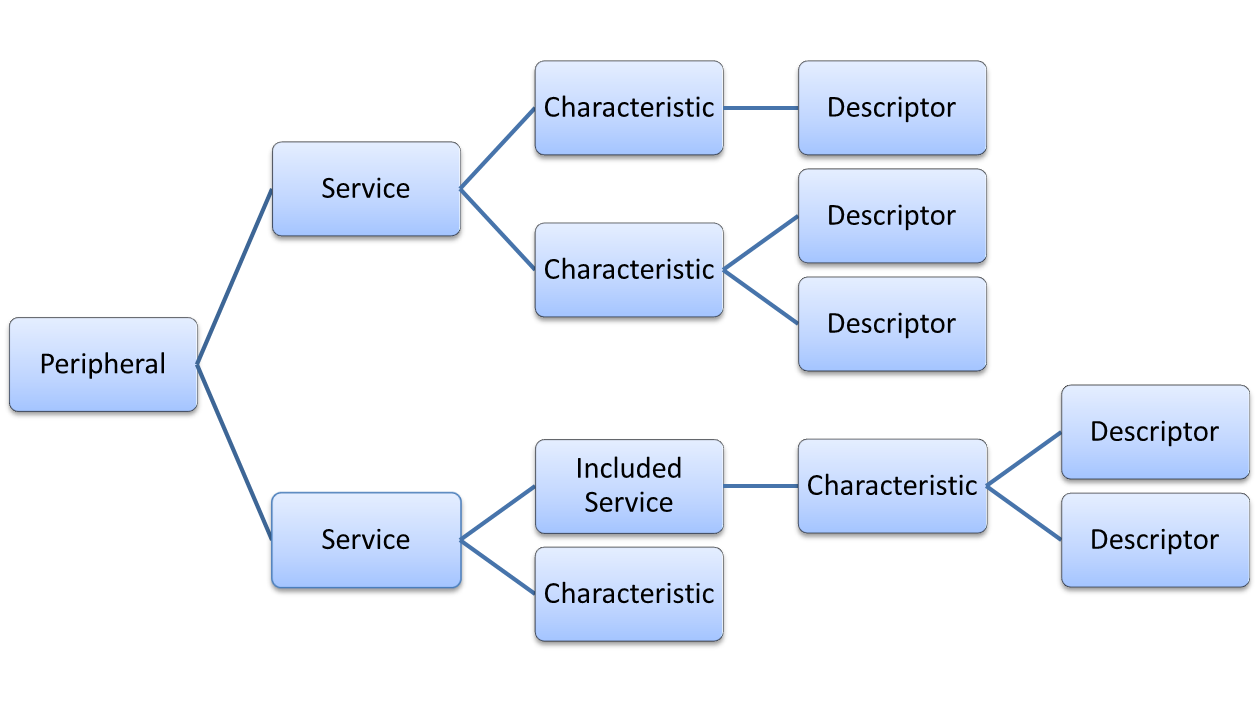
A characteristic is the principal information carrier. It has a
value()andproperties()describing the access permissions for the value. The general purpose of the contained descriptor is to further define the nature of the characteristic. For example, it might specify how the value is meant to be interpreted or whether it can notify the value consumer about value changes.Service Interaction#
Once a service object was created for the first time, its details are yet to be discovered. This is indicated by its current
state()beingDiscoveryRequired. It is only possible to retrieve theserviceUuid()andserviceName().The discovery of its included services, characteristics and descriptors is triggered when calling
discoverDetails(). During the discovery thestate()transitions fromDiscoveryRequiredviaDiscoveringServiceto its finalServiceDiscoveredstate. This transition is advertised via thestateChanged()signal. Once the details are known, all of the contained characteristics, descriptors and included services are known and can be read or written.The values of characteristics and descriptors can be retrieved via
QLowEnergyCharacteristicandQLowEnergyDescriptor, respectively. However, direct reading or writing of these attributes requires the service object. ThereadCharacteristic()function attempts to re-read the value of a characteristic. Although the initial service discovery may have obtained a value already this call may be required in cases where the characteristic value constantly changes without any notifications being provided. An example might be a time characteristic that provides a continuous value. If the read attempt is successful, thecharacteristicRead()signal is emitted. A failure to read the value triggers theCharacteristicReadError. ThewriteCharacteristic()function attempts to write a new value to the given characteristic. If the write attempt is successful, thecharacteristicWritten()signal is emitted. A failure to write triggers theCharacteristicWriteError. Reading and writing of descriptors follows the same pattern.Every attempt is made to read or write the value of a descriptor or characteristic on the hardware. This means that meta information such as
properties()is generally ignored when reading and writing. As an example, it is possible to callwriteCharacteristic()despite the characteristic being read-only based on its meta data description. The resulting write request is forwarded to the connected device and it is up to the device to respond to the potentially invalid request. In this case the result is the emission of theCharacteristicWriteErrorin response to the returned device error. This behavior simplifies interaction with devices which report wrong meta information. If it was not possible to forward the request to the remote device theOperationErroris set. A potential reason could be that the to-be-written characteristic object does not even belong the current service. In summary, the two types of errors permit a quick distinction of local and remote error cases.All requests are serialised based on First-In First-Out principle. For example, issuing a second write request, before the previous write request has finished, is delayed until the first write request has finished.
Note
Currently, it is not possible to send signed write or reliable write requests.
In some cases the peripheral generates value updates which the central is interested in receiving. In order for a characteristic to support such notifications it must have the
NotifyorIndicateproperty and a descriptor of typeClientCharacteristicConfiguration. Provided those conditions are fulfilled notifications can be enabled as shown in the following code segment:#PreCondition: service details already discovered batteryLevel = service.characteristic( QBluetoothUuid.CharacteristicType.BatteryLevel) if not batteryLevel.isValid(): return notification = batteryLevel.descriptor( QBluetoothUuid.DescriptorType.ClientCharacteristicConfiguration) if not notification.isValid(): return # establish hook into notifications connect(service, SIGNAL(characteristicChanged(QLowEnergyCharacteristic,QByteArray)), self, SLOT(characteristicChanged(QLowEnergyCharacteristic,QByteArray))) # enable notification service.writeDescriptor(notification, QByteArray.fromHex("0100")) # disable notification #service->writeDescriptor(notification, QByteArray::fromHex("0000")) # wait until descriptorWritten() signal is emitted # to confirm successful write
The example shows a battery level characteristic which updates the central on every value change. The notifications are provided via the
characteristicChanged()signal. More details about this mechanism are provided by the Bluetooth Specification .Service Data Sharing#
Each
QLowEnergyServiceinstance shares its internal states and information with otherQLowEnergyServiceinstance of the same service. If one instance initiates the discovery of the service details, all remaining instances automatically follow. Therefore the following snippet always works:first, = QLowEnergyService() control = QLowEnergyController(remoteDevice) control.connectToDevice() # waiting for connection first = control.createServiceObject(QBluetoothUuid.ServiceClassUuid.BatteryService) second = control.createServiceObject(QBluetoothUuid.ServiceClassUuid.BatteryService) Q_ASSERT(first.state() == QLowEnergyService.RemoteService) Q_ASSERT(first.state() == second.state()) first.discoverDetails() Q_ASSERT(first.state() == QLowEnergyService.RemoteServiceDiscovering) Q_ASSERT(first.state() == second.state())
Other operations such as calls to
readCharacteristic(),readDescriptor(),writeCharacteristic(),writeDescriptor()or the invalidation of the service due to the relatedQLowEnergyControllerdisconnecting from the device are shared the same way.- class ServiceType#
(inherits
enum.Flag) This enum describes the type of the service.Constant
Description
QLowEnergyService.PrimaryService
The service is a top-level/primary service. If this type flag is not set, the service is considered to be a secondary service. Each service may be included by another service which is indicated by IncludedService.
QLowEnergyService.IncludedService
The service is included by another service. On some platforms, this flag cannot be determined until the service that includes the current service was discovered.
- class ServiceError#
This enum describes all possible error conditions during the service’s existence. The
error()function returns the last occurred error.Constant
Description
QLowEnergyService.NoError
No error has occurred.
QLowEnergyService.OperationError
An operation was attempted while the service was not ready. An example might be the attempt to write to the service while it was not yet in the
ServiceDiscoveredstate()or the service is invalid due to a loss of connection to the peripheral device.QLowEnergyService.CharacteristicReadError
An attempt to read a characteristic value failed. For example, it might be triggered in response to a call to
readCharacteristic().QLowEnergyService.CharacteristicWriteError
An attempt to write a new value to a characteristic failed. For example, it might be triggered when attempting to write to a read-only characteristic.
QLowEnergyService.DescriptorReadError
An attempt to read a descriptor value failed. For example, it might be triggered in response to a call to
readDescriptor().QLowEnergyService.DescriptorWriteError
An attempt to write a new value to a descriptor failed. For example, it might be triggered when attempting to write to a read-only descriptor.
QLowEnergyService.UnknownError
An unknown error occurred when interacting with the service.
- class ServiceState#
This enum describes the
state()of the service object.Constant
Description
QLowEnergyService.InvalidService
A service can become invalid when it looses the connection to the underlying device. Even though the connection may be lost it retains its last information. An invalid service cannot become valid anymore even if the connection to the device is re-established.
QLowEnergyService.RemoteService
The service details are yet to be discovered by calling
discoverDetails(). The only reliable pieces of information are itsserviceUuid()andserviceName().QLowEnergyService.RemoteServiceDiscovering
The service details are being discovered.
QLowEnergyService.RemoteServiceDiscovered
The service details have been discovered.
QLowEnergyService.LocalService
The service is associated with a controller object in the
peripheral role. Such service objects do not change their state.QLowEnergyService.DiscoveryRequired
Deprecated. Was renamed to RemoteService.
QLowEnergyService.DiscoveringService
Deprecated. Was renamed to RemoteServiceDiscovering.
QLowEnergyService.ServiceDiscovered
Deprecated. Was renamed to RemoteServiceDiscovered.
- class DiscoveryMode#
This enum lists service discovery modes. All modes discover the characteristics of the service and the descriptors of the characteristics. The modes differ in whether characteristic values and descriptors are read.
Constant
Description
QLowEnergyService.FullDiscovery
During a full discovery, all characteristics are discovered. All characteristic values and descriptors are read.
QLowEnergyService.SkipValueDiscovery
During a minimal discovery, all characteristics are discovered. Characteristic values and descriptors are not read.
See also
- class WriteMode#
This enum describes the mode to be used when writing a characteristic value. The characteristic advertises its supported write modes via its
properties.Constant
Description
QLowEnergyService.WriteWithResponse
If a characteristic is written using this mode, the peripheral shall send a write confirmation. If the operation is successful, the confirmation is emitted via the
characteristicWritten()signal. Otherwise theCharacteristicWriteErroris emitted. A characteristic must have set theWriteproperty to support this write mode.QLowEnergyService.WriteWithoutResponse
If a characteristic is written using this mode, the remote peripheral shall not send a write confirmation. The operation’s success cannot be determined and the payload must not be longer than 20 bytes. A characteristic must have set the
WriteNoResponseproperty to support this write mode. Its adavantage is a quicker write operation as it may happen in between other device interactions.QLowEnergyService.WriteSigned
If a characteristic is written using this mode, the remote peripheral shall not send a write confirmation. The operation’s success cannot be determined and the payload must not be longer than 8 bytes. A bond must exist between the two devices and the link must not be encrypted. A characteristic must have set the
WriteSignedproperty to support this write mode. This value is currently only supported on Android and on Linux with BlueZ 5 and a kernel version 3.7 or newer.
- characteristic(uuid)#
- Parameters:
uuid –
QBluetoothUuid- Return type:
Returns the matching characteristic for
uuid; otherwise an invalid characteristic.The returned characteristic is invalid if this service instance’s
discoverDetails()was not yet called or there are no characteristics with a matchinguuid.See also
- characteristicChanged(info, value)#
- Parameters:
info –
QLowEnergyCharacteristicvalue –
QByteArray
If the associated controller object is in the
centralrole, this signal is emitted when the value ofcharacteristicis changed by an event on the peripheral/device side. In that case, the signal emission implies that change notifications must have been activated via the characteristic’sClientCharacteristicConfigurationdescriptor prior to the change event on the peripheral. More details on how this might be done can be found furtherabove.If the controller is in the
peripheralrole, that is, the service object was created viaaddService, the signal is emitted when a GATT client has written the value of the characteristic using a write request or command.The
newValueparameter contains the updated value of thecharacteristic.- characteristicRead(info, value)#
- Parameters:
info –
QLowEnergyCharacteristicvalue –
QByteArray
This signal is emitted when the read request for
characteristicsuccessfully returned itsvalue. The signal might be triggered by calling characteristicRead(). If the read operation is not successful, theerrorOccurred()signal is emitted using theCharacteristicReadErrorflag.- characteristicWritten(info, value)#
- Parameters:
info –
QLowEnergyCharacteristicvalue –
QByteArray
This signal is emitted when the value of
characteristicis successfully changed tonewValue. The change must have been triggered by callingwriteCharacteristic(). If the write operation is not successful, theerrorOccurred()signal is emitted using theCharacteristicWriteErrorflag.The reception of the written signal can be considered as a sign that the target device received the to-be-written value and reports back the status of write request.
Note
If
writeCharacteristic()is called using theWriteWithoutResponsemode, this signal and theerrorOccurred()are never emitted.- characteristics()#
- Return type:
.list of QLowEnergyCharacteristic
Returns all characteristics associated with this
QLowEnergyServiceinstance.The returned list is empty if this service instance’s
discoverDetails()was not yet called or there are no known characteristics.See also
- contains(characteristic)#
- Parameters:
characteristic –
QLowEnergyCharacteristic- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueifcharacteristicbelongs to this service; otherwisefalse.A characteristic belongs to a service if
characteristics()contains thecharacteristic.- contains(descriptor)
- Parameters:
descriptor –
QLowEnergyDescriptor- Return type:
bool
Returns
trueifdescriptorbelongs to this service; otherwisefalse.- descriptorRead(info, value)#
- Parameters:
info –
QLowEnergyDescriptorvalue –
QByteArray
This signal is emitted when the read request for
descriptorsuccessfully returned itsvalue. The signal might be triggered by calling descriptorRead(). If the read operation is not successful, theerrorOccurred()signal is emitted using theDescriptorReadErrorflag.- descriptorWritten(info, value)#
- Parameters:
info –
QLowEnergyDescriptorvalue –
QByteArray
This signal is emitted when the value of
descriptoris successfully changed tonewValue. If the associated controller object is in thecentralrole, the change must have been caused by callingwriteDescriptor(). Otherwise, the signal is the result of a write request or command from a GATT client to the respective descriptor.See also
- discoverDetails([mode=QLowEnergyService.DiscoveryMode.FullDiscovery])#
- Parameters:
mode –
DiscoveryMode
Initiates discovery of the service’s included services, characteristics, and their associated descriptors.
The discovery process is indicated via the
stateChanged()signal. After creation, the service is inDiscoveryRequiredstate. When calling discoverDetails() it transitions toDiscoveringService. After completion of detail discovery, it transitions toServiceDiscoveredstate. On each transition, thestateChanged()signal is emitted. Depending on the argumentmode, aFullDiscoveryor aSkipValueDiscoveryis performed. In any case, all services and characteristics are discovered. AFullDiscoveryproceeds and reads all characteristic values and descriptors. ASkipValueDiscoverydoes not read characteristic values and descriptors. ASkipValueDiscoveryhas two advantages. First, it is faster. Second, it circumvents bugs in some devices which wrongly advertise characteristics or descriptors as readable but nevertheless do not permit reads on them. This can trigger unpredictable behavior. After aSkipValueDiscovery, it is necessary to callreadCharacteristic()/readDescriptor()and wait for them to finish successfully before accessing the value of a characteristic or descriptor.The argument
modewas introduced in Qt 6.2.See also
- error()#
- Return type:
Returns the last occurred error or
NoError.- errorOccurred(error)#
- Parameters:
error –
ServiceError
This signal is emitted when an error occurrs. The
newErrorparameter describes the error that occurred.- includedServices()#
- Return type:
.list of QBluetoothUuid
Returns the UUIDs of all services which are included by the current service.
The returned list is empty if this service instance’s
discoverDetails()was not yet called or there are no known characteristics.It is possible that an included service contains yet another service. Such second level includes have to be obtained via their relevant first level
QLowEnergyServiceinstance. Technically, this could create a circular dependency.createServiceObject()should be used to obtain service instances for each of the UUIDs.See also
- readCharacteristic(characteristic)#
- Parameters:
characteristic –
QLowEnergyCharacteristic
Reads the value of
characteristic. If the operation is successful, thecharacteristicRead()signal is emitted; otherwise theCharacteristicReadErroris set. In general, acharacteristicis readable, if itsReadproperty is set.All descriptor and characteristic requests towards the same remote device are serialised. A queue is employed when issuing multiple requests at the same time. The queue does not eliminate duplicated read requests for the same characteristic.
A characteristic can only be read if the service is in the
ServiceDiscoveredstate and belongs to the service. If one of these conditions is not true theOperationErroris set.Note
Calling this function despite
properties()reporting a non-readable property always attempts to read the characteristic’s value on the hardware. If the hardware returns with an error theCharacteristicReadErroris set.- readDescriptor(descriptor)#
- Parameters:
descriptor –
QLowEnergyDescriptor
Reads the value of
descriptor. If the operation is successful, thedescriptorRead()signal is emitted; otherwise theDescriptorReadErroris set.All descriptor and characteristic requests towards the same remote device are serialised. A queue is employed when issuing multiple requests at the same time. The queue does not eliminate duplicated read requests for the same descriptor.
A descriptor can only be read if the service is in the
ServiceDiscoveredstate and the descriptor belongs to the service. If one of these conditions is not true theOperationErroris set.See also
- serviceName()#
- Return type:
str
Returns the name of the service; otherwise an empty string.
The returned name can only be retrieved if
serviceUuid()is a well-known UUID .- serviceUuid()#
- Return type:
Returns the UUID of the service; otherwise a null UUID.
- state()#
- Return type:
Returns the current state of the service.
If the device’s service was instantiated for the first time, the object’s state is
DiscoveryRequired. The state of all service objects which point to the same service on the peripheral device are always equal. This is caused by the shared nature of the internal object data. Therefore any service object instance created after the first one has a state equal to already existing instances.A service becomes invalid if the
QLowEnergyControllerdisconnects from the remote device. An invalid service retains its internal state at the time of the disconnect event. This implies that once the service details are discovered they can even be retrieved from an invalid service. This permits scenarios where the device connection is established, the service details are retrieved and the device immediately disconnected to permit the next device to connect to the peripheral device.However, under normal circumstances the connection should remain to avoid repeated discovery of services and their details. The discovery may take a while and the client can subscribe to ongoing change notifications.
See also
- stateChanged(newState)#
- Parameters:
newState –
ServiceState
This signal is emitted when the service’s state changes. The
newStatecan also be retrieved viastate().See also
- type()#
- Return type:
Combination of
ServiceType
Returns the type of the service.
Note
The type attribute cannot be relied upon until the service has reached the
ServiceDiscoveredstate. This field is initialised withPrimaryService.Note
On Android, it is not possible to determine whether a service is a primary or secondary service. Therefore all services have the
PrimaryServiceflag set.- writeCharacteristic(characteristic, newValue[, mode=QLowEnergyService.WriteMode.WriteWithResponse])#
- Parameters:
characteristic –
QLowEnergyCharacteristicnewValue –
QByteArraymode –
WriteMode
Writes
newValueas value for thecharacteristic. The exact semantics depend on the role that the associated controller object is in.Central role
The call results in a write request or command to a remote peripheral. If the operation is successful, the
characteristicWritten()signal is emitted; otherwise theCharacteristicWriteErroris set. Calling this function does not trigger the acharacteristicChanged()signal unless the peripheral itself changes the value again after the current write request.The
modeparameter determines whether the remote device should send a write confirmation. The to-be-writtencharacteristicmust support the relevant write mode. The characteristic’s supported write modes are indicated by itsWriteandWriteNoResponseproperties.All descriptor and characteristic write requests towards the same remote device are serialised. A queue is employed when issuing multiple write requests at the same time. The queue does not eliminate duplicated write requests for the same characteristic. For example, if the same descriptor is set to the value A and immediately afterwards to B, the two write request are executed in the given order.
Note
Currently, it is not possible to use signed or reliable writes as defined by the Bluetooth specification.
A characteristic can only be written if this service is in the
ServiceDiscoveredstate and belongs to the service. If one of these conditions is not true theOperationErroris set.Note
Calling this function despite
properties()reporting a non-writable property always attempts to write to the hardware. Similarly, aWriteWithoutResponseis sent to the hardware too although the characteristic may only supportWriteWithResponse. If the hardware returns with an error theCharacteristicWriteErroris set.Peripheral role
The call results in the value of the characteristic getting updated in the local database.
If a client is currently connected and it has enabled notifications or indications for the characteristic, the respective information will be sent. If a device has enabled notifications or indications for the characteristic and that device is currently not connected, but a bond exists between it and the local device, then the notification or indication will be sent on the next reconnection.
If there is a constraint on the length of the characteristic value and
newValuedoes not adhere to that constraint, the behavior is unspecified.Note
The
modeargument is ignored in peripheral mode.- writeDescriptor(descriptor, newValue)#
- Parameters:
descriptor –
QLowEnergyDescriptornewValue –
QByteArray
Writes
newValueas value fordescriptor. The exact semantics depend on the role that the associated controller object is in.Central role
A call to this function results in a write request to the remote device. If the operation is successful, the
descriptorWritten()signal is emitted; otherwise theDescriptorWriteErroris emitted.All descriptor and characteristic requests towards the same remote device are serialised. A queue is employed when issuing multiple write requests at the same time. The queue does not eliminate duplicated write requests for the same descriptor. For example, if the same descriptor is set to the value A and immediately afterwards to B, the two write request are executed in the given order.
A descriptor can only be written if this service is in the
ServiceDiscoveredstate, belongs to the service. If one of these conditions is not true theOperationErroris set.Peripheral Role
The value is written to the local service database. If the contents of
newValueare not valid fordescriptor, the behavior is unspecified.See also