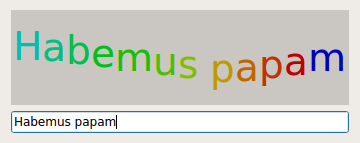
Wiggly Example¶
The Wiggly example shows how to animate a widget using QBasicTimer and timerEvent() . In addition, the example demonstrates how to use QFontMetrics to determine the size of text on screen.
QBasicTimer is a low-level class for timers. Unlike QTimer , QBasicTimer doesn’t inherit from QObject ; instead of emitting a timeout() signal when a certain amount of time has passed, it sends a QTimerEvent to a QObject of our choice. This makes QBasicTimer a more lightweight alternative to QTimer . Qt’s built-in widgets use it internally, and it is provided in Qt’s API for highly-optimized applications (such as embedded applications).
The example consists of two classes:
WigglyWidgetis the custom widget displaying the text in a wiggly line.
Dialogis the dialog widget allowing the user to enter a text. It combines aWigglyWidgetand aQLineEdit.
We will first take a quick look at the Dialog class, then we will review the WigglyWidget class.
Dialog Class Definition¶
class Dialog(QDialog): Q_OBJECT # public Dialog = explicit(QWidget parent = None)
The Dialog class provides a dialog widget that allows the user to enter a text. The text is then rendered by WigglyWidget.
Dialog Class Implementation¶
def __init__(self, parent): QDialog.__init__(self, parent) wigglyWidget = WigglyWidget() lineEdit = QLineEdit() layout = QVBoxLayout(self) layout.addWidget(wigglyWidget) layout.addWidget(lineEdit) connect(lineEdit, QLineEdit.textChanged, wigglyWidget, WigglyWidget.setText) lineEdit.setText(tr("Hello world!")) setWindowTitle(tr("Wiggly")) resize(360, 145)
In the constructor we create a wiggly widget along with a line edit , and we put the two widgets in a vertical layout. We connect the line edit’s textChanged() signal to the wiggly widget’s setText() slot to obtain the real time interaction with the wiggly widget. The widget’s default text is “Hello world!”.
WigglyWidget Class Definition¶
class WigglyWidget(QWidget): Q_OBJECT # public WigglyWidget(QWidget parent = None) slots: = public() def setText(newText): text = newText protected: def paintEvent(event): def timerEvent(event): # private timer = QBasicTimer() text = QString() step = int()
The WigglyWidget class provides the wiggly line displaying the text. We subclass QWidget and reimplement the standard paintEvent() and timerEvent() functions to draw and update the widget. In addition we implement a public setText() slot that sets the widget’s text.
The timer variable, of type QBasicTimer , is used to update the widget at regular intervals, making the widget move. The text variable is used to store the currently displayed text, and step to calculate position and color for each character on the wiggly line.
WigglyWidget Class Implementation¶
def __init__(self, parent): QWidget.__init__(self, parent) self.step = 0 setBackgroundRole(QPalette.Midlight) setAutoFillBackground(True) newFont = font() newFont.setPointSize(newFont.pointSize() + 20) setFont(newFont) timer.start(60, self)
In the constructor, we make the widget’s background slightly lighter than the usual background using the Midlight color role. The background role defines the brush from the widget’s palette that Qt uses to paint the background. Then we enlarge the widget’s font with 20 points.
Finally we start the timer; the call to start() makes sure that this particular wiggly widget will receive the timer events generated when the timer times out (every 60 milliseconds).
def paintEvent(self, */): staticexpr int sineTable[16] = { 0, 38, 71, 92, 100, 92, 71, 38, 0, -38, -71, -92, -100, -92, -71, -38 metrics = QFontMetrics(font()) x = (width() - metrics.horizontalAdvance(text)) / 2 y = (height() + metrics.ascent() - metrics.descent()) / 2 color = QColor()
The paintEvent() function is called whenever a QPaintEvent is sent to the widget. Paint events are sent to widgets that need to update themselves, for instance when part of a widget is exposed because a covering widget was moved. For the wiggly widget, a paint event will also be generated every 60 milliseconds from the timerEvent() slot.
The sineTable represents y-values of the sine curve, multiplied by 100. It is used to make the wiggly widget move along the sine curve.
The QFontMetrics object provides information about the widget’s font. The x variable is the horizontal position where we start drawing the text. The y variable is the vertical position of the text’s base line. Both variables are computed so that the text is horizontally and vertically centered. To compute the base line, we take into account the font’s ascent (the height of the font above the base line) and font’s descent (the height of the font below the base line). If the descent equals the ascent, they cancel out each other and the base line is at height() / 2.
painter = QPainter(self) for i in range(0, text.size()): index = (step + i) % 16 color.setHsv((15 - index) * 16, 255, 191) painter.setPen(color) painter.drawText(x, y - ((sineTable[index] * metrics.height()) / 400), QString(text[i])) x += metrics.horizontalAdvance(text[i])
Each time the paintEvent() function is called, we create a QPainter object painter to draw the contents of the widget. For each character in text, we determine the color and the position on the wiggly line based on step. In addition, x is incremented by the character’s width.
For simplicity, we assume that horizontalAdvance (text) returns the sum of the individual character advances ( horizontalAdvance (text[i])). In practice, this is not always the case because horizontalAdvance (text) also takes into account the kerning between certain letters (e.g., ‘A’ and ‘V’). The result is that the text isn’t perfectly centered. You can verify this by typing “AVAVAVAVAVAV” in the line edit.
def timerEvent(self, event): if (event.timerId() == timer.timerId()) { step = step + 1 update() else: QWidget.timerEvent(event)
The timerEvent() function receives all the timer events that are generated for this widget. If a timer event is sent from the widget’s QBasicTimer , we increment step to make the text move, and call update() to refresh the display. Any other timer event is passed on to the base class’s implementation of the timerEvent() function.
The update() slot does not cause an immediate repaint; instead the slot schedules a paint event for processing when Qt returns to the main event loop. The paint events are then handled by WigglyWidget's paintEvent() function.
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.