Flow Layout Example¶
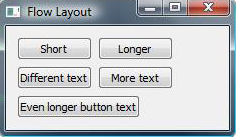
Flow Layout implements a layout that handles different window sizes in a Qt Widgets application. The widget placement changes depending on the width of the application window.
"""PySide6 port of the widgets/layouts/flowlayout example from Qt v6.x"""
import sys
from PySide6.QtCore import Qt, QMargins, QPoint, QRect, QSize
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QLayout, QPushButton, QSizePolicy, QWidget
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
flow_layout = FlowLayout(self)
flow_layout.addWidget(QPushButton("Short"))
flow_layout.addWidget(QPushButton("Longer"))
flow_layout.addWidget(QPushButton("Different text"))
flow_layout.addWidget(QPushButton("More text"))
flow_layout.addWidget(QPushButton("Even longer button text"))
self.setWindowTitle("Flow Layout")
class FlowLayout(QLayout):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super().__init__(parent)
if parent is not None:
self.setContentsMargins(QMargins(0, 0, 0, 0))
self._item_list = []
def __del__(self):
item = self.takeAt(0)
while item:
item = self.takeAt(0)
def addItem(self, item):
self._item_list.append(item)
def count(self):
return len(self._item_list)
def itemAt(self, index):
if 0 <= index < len(self._item_list):
return self._item_list[index]
return None
def takeAt(self, index):
if 0 <= index < len(self._item_list):
return self._item_list.pop(index)
return None
def expandingDirections(self):
return Qt.Orientation(0)
def hasHeightForWidth(self):
return True
def heightForWidth(self, width):
height = self._do_layout(QRect(0, 0, width, 0), True)
return height
def setGeometry(self, rect):
super(FlowLayout, self).setGeometry(rect)
self._do_layout(rect, False)
def sizeHint(self):
return self.minimumSize()
def minimumSize(self):
size = QSize()
for item in self._item_list:
size = size.expandedTo(item.minimumSize())
size += QSize(2 * self.contentsMargins().top(), 2 * self.contentsMargins().top())
return size
def _do_layout(self, rect, test_only):
x = rect.x()
y = rect.y()
line_height = 0
spacing = self.spacing()
for item in self._item_list:
style = item.widget().style()
layout_spacing_x = style.layoutSpacing(
QSizePolicy.PushButton, QSizePolicy.PushButton, Qt.Horizontal
)
layout_spacing_y = style.layoutSpacing(
QSizePolicy.PushButton, QSizePolicy.PushButton, Qt.Vertical
)
space_x = spacing + layout_spacing_x
space_y = spacing + layout_spacing_y
next_x = x + item.sizeHint().width() + space_x
if next_x - space_x > rect.right() and line_height > 0:
x = rect.x()
y = y + line_height + space_y
next_x = x + item.sizeHint().width() + space_x
line_height = 0
if not test_only:
item.setGeometry(QRect(QPoint(x, y), item.sizeHint()))
x = next_x
line_height = max(line_height, item.sizeHint().height())
return y + line_height - rect.y()
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
main_win = Window()
main_win.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
© 2022 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
